Markets VS global Rates
Global interest rates play a crucial role in shaping financial markets and influencing investment decisions worldwide. The relationship between interest rates and market performance is complex, with sudden rises in rates often putting strain on market dynamics. This article examines the interplay between markets and global interest rates, focusing on the challenges that arise when rates experience a rapid increase.
Understanding the Relationship
- Interest Rates and Market Performance: Interest rates impact various aspects of the economy, including borrowing costs, consumer spending, and investment decisions. Changes in interest rates can influence market sentiment, valuation of assets, and risk appetite among investors.
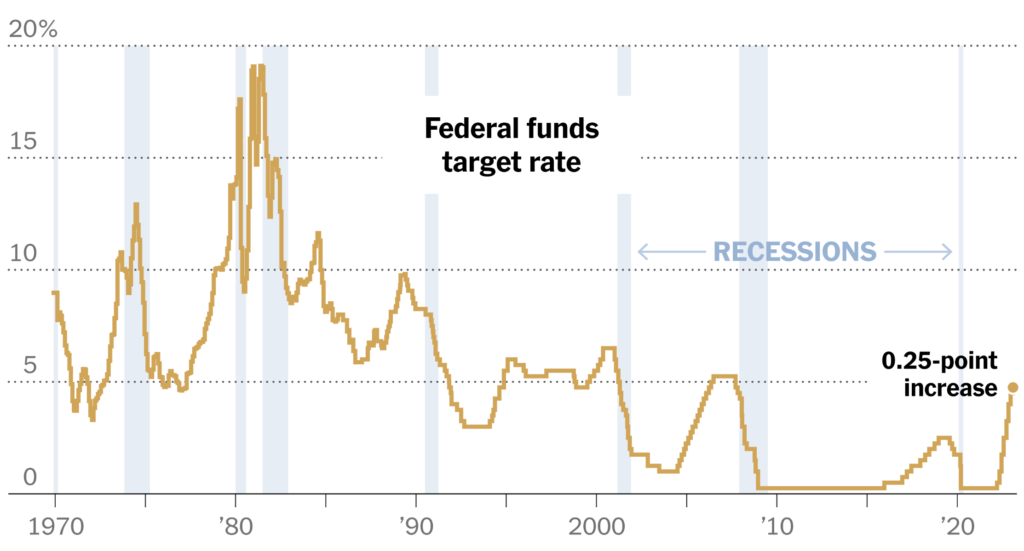
- Monetary Policy: Central banks employ monetary policy tools, such as adjusting benchmark interest rates, to manage inflation, stimulate economic growth, or curb excessive borrowing. Policy changes by major central banks can have ripple effects across global markets.
- Bond Market and Yield Movements: Changes in interest rates affect bond prices and yields. When rates rise, bond prices tend to fall, leading to potential capital losses for bondholders. Yield movements impact borrowing costs for governments, corporations, and individuals, influencing investment decisions and market liquidity.

The Sudden Rise of Rates and Market Strain
- Impact on Equity Markets: A sudden and significant increase in interest rates can trigger a reevaluation of equity valuations. Higher rates may make borrowing more expensive, impacting corporate earnings and growth prospects. This can result in increased volatility, equity sell-offs, and a shift towards more conservative investments.
- Bond Market Turmoil: Rising rates may lead to a sell-off in the bond market as investors seek higher yields elsewhere. This can cause bond prices to decline sharply and yields to rise rapidly. Bond market turmoil can create challenges for fixed-income investors, including reduced returns and potential capital losses.
- Currency Fluctuations: Sharp increases in interest rates can attract capital flows into a country, strengthening its currency. This can adversely impact export-oriented economies, as a stronger currency makes their goods relatively more expensive, potentially leading to reduced competitiveness and trade imbalances.
- Financial Stress and Debt Servicing: Sudden rate hikes can strain highly indebted individuals, corporations, and governments, increasing the cost of servicing existing debt. This can lead to financial stress, defaults, and a tightening of credit conditions, further impacting market stability.
Navigating the Challenges
- Monitoring Central Bank Communications: Staying abreast of central bank communications and policy announcements is crucial for market participants. Clarity on the direction and pace of interest rate changes can help investors anticipate market reactions and adjust their strategies accordingly.
- Diversification and Risk Management: Maintaining a diversified investment portfolio can help mitigate risks associated with sudden rate increases. Allocating assets across different asset classes and geographies can provide a buffer against volatility and potential losses.
- Adaptability and Flexibility: Being adaptable to changing market conditions is essential. Investors and businesses should be prepared to adjust their investment strategies, consider alternative investment options, and monitor the impact of rate changes on their portfolios.
Conclusion
The relationship between markets and global interest rates is intricate, with sudden increases in rates often straining market dynamics. Interest rate movements impact market sentiment, asset valuations, borrowing costs, and investor behavior. A rapid rise in rates can lead to challenges in equity and bond markets, currency fluctuations, financial stress, and debt servicing issues. Navigating these challenges requires monitoring central bank communications, diversification, risk management, and adaptability. By understanding the interplay between rates and markets, investors and businesses can better position themselves to weather sudden rate increases and make informed decisions in a dynamic global environment.




